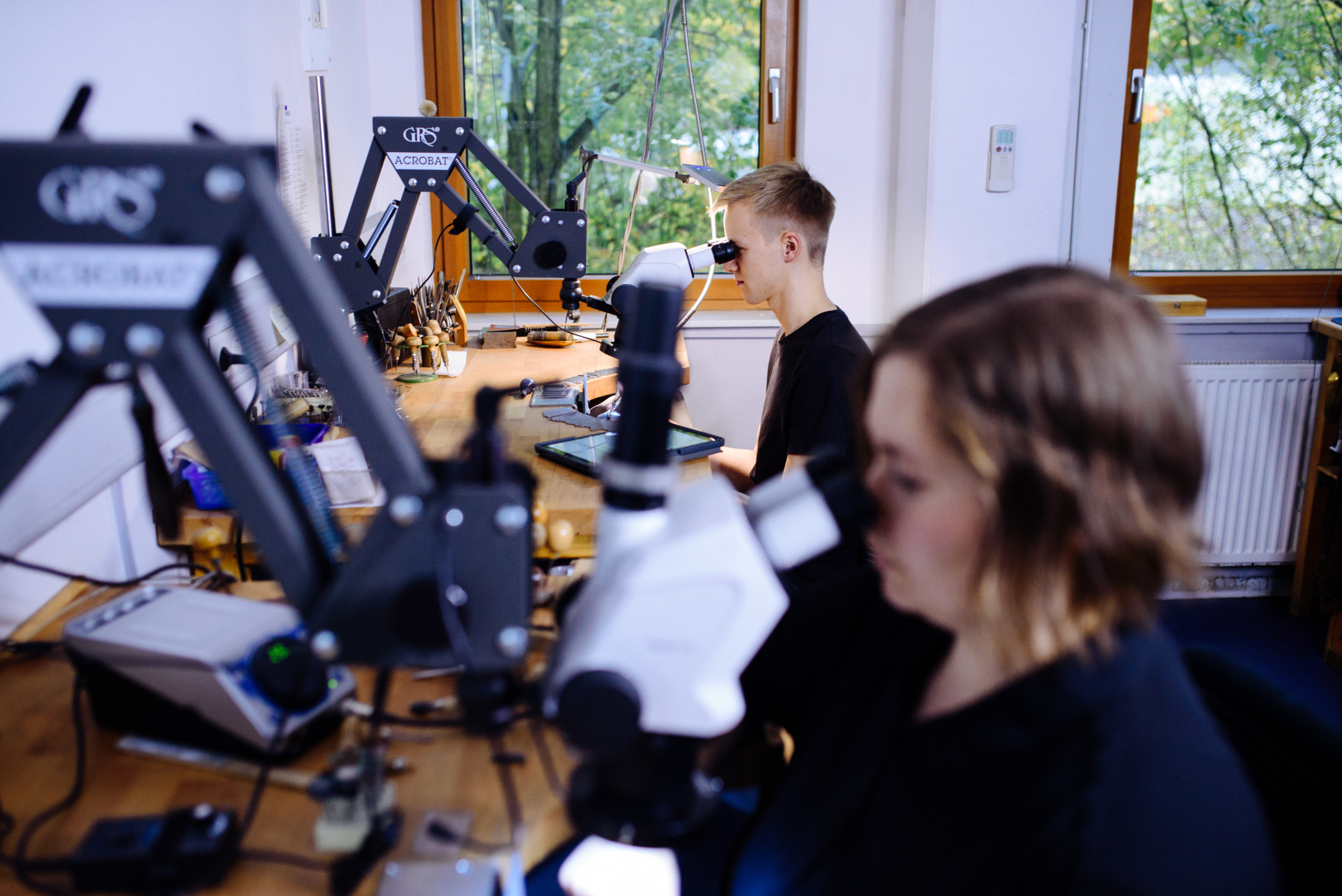
Our experienced gem setters are experts in combining your rings with your gemstones into pieces of jewelery of unmistakable grace.
Ring bands become pieces of jewelry


It is our aim to offer you, our customer, the full range of services and products related to wedding and jewelry rings. It goes without saying that we have our own stone setting facility where we can add all kinds of gemstones to our rings. Our experienced gem setters, some of whom have been part of our team for over 20 years, are true masters of this ancient craft.
Setting type
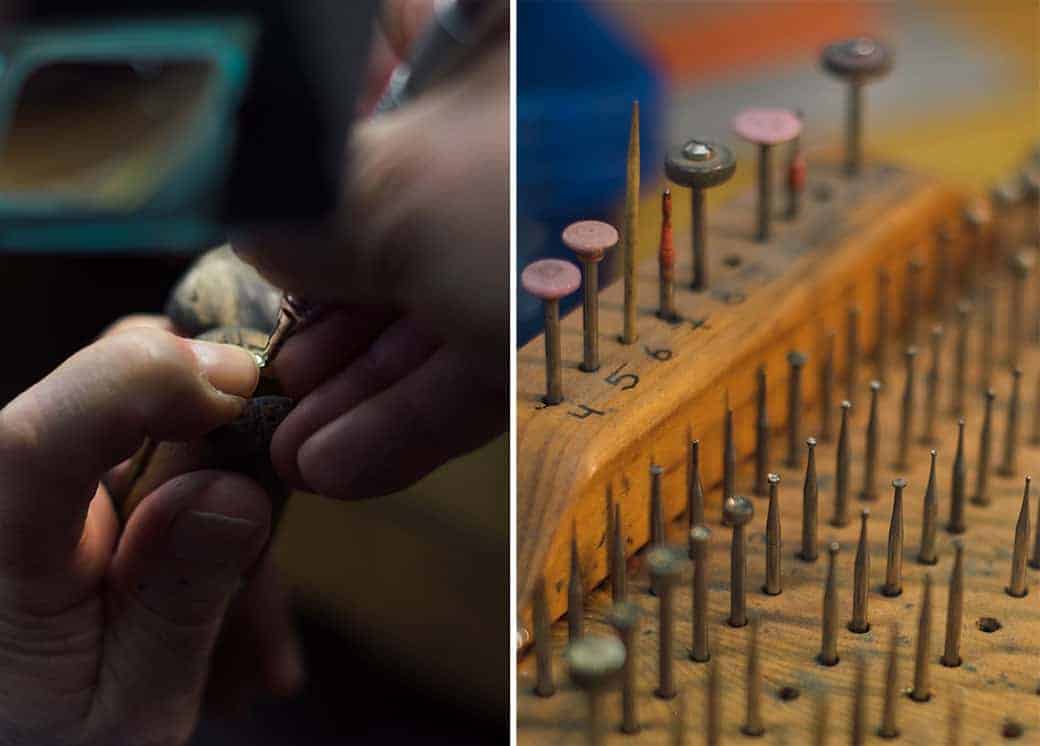
Traditionally there are different ways of adding precious stones to rings and other pieces of jewelry. We offer you all common of these so-called “barrel types”. Our experienced team can also implement the most individual customer requests.

 |
Claw settingIn this setting, also known as the chaton setting, the stone sits high on the ring, it is supported on the ring by fine metal sticks (claws). In order to give the stone a good setting, the prongs on the upper edge are pierced inwards or milled and the part of the prong that has remained is pressed over the stone and filed. This type of setting is often found on solitaire rings. |
 |
BezelWhen rubbed in, the gemstone is embedded in a flat plate and only held in place by “rubbing” the edge of the surrounding metal a little over the edge of the cut stone becomes. This type of setting is particularly suitable for small stones and is very popular with wedding rings, as only a narrow precious metal edge covers the stone and this type of setting has a high degree of durability and is therefore suitable for everyday use due to the "unity with the ring". |
 |
Tension typeWith the tension setting type, the precious stones are clamped into the rings - as the name suggests. To do this, an area of the ring is cut out by our experts and the metal is compacted at this point to create a stone seat. This compression of the stone seat has the consequence that the stone does not wobble and sits firmly in the ring. |
 |
BeadWhen grasping the stones in the scrap, the gemstone is inserted into a milled hole and the precious metal is compressed with a graver in such a way that shavings are created, which then over the Pass the gemstone and thus fix it. Stones can be set individually or in a row. This type of setting also forms a "unit with the ring", which results in a high level of durability and thus suitability for everyday use. |
 |
Channel settingSimilar to the clamping setting type, the gemstones are also clamped into the ring with the channel setting. For this purpose, the metal in this type of setting is compacted where the gemstones sit - in the stone seat. The compression means that the gemstones do not wobble and are firmly set in the ring. With channel settings, several gemstones are lined up one behind the other in a joint (channel). Because the gemstones are set in this type of setting, so to speak, "floating", the light is reflected with maximum brilliance. Thanks to the “channel”, this type of setting still has a high degree of durability and suitability for everyday use and is therefore very suitable for wedding rings. |
In order to achieve the highest possible quality, we also rely on the close interplay of the most modern technology and real craftsmanship with diamonds. In order to determine ideal stones for certain applications in order to set them partially automatically in a later work step, we rely on automatic, digital stone measurement with the Benzinger FourC stone measurement machine.
Gemstones
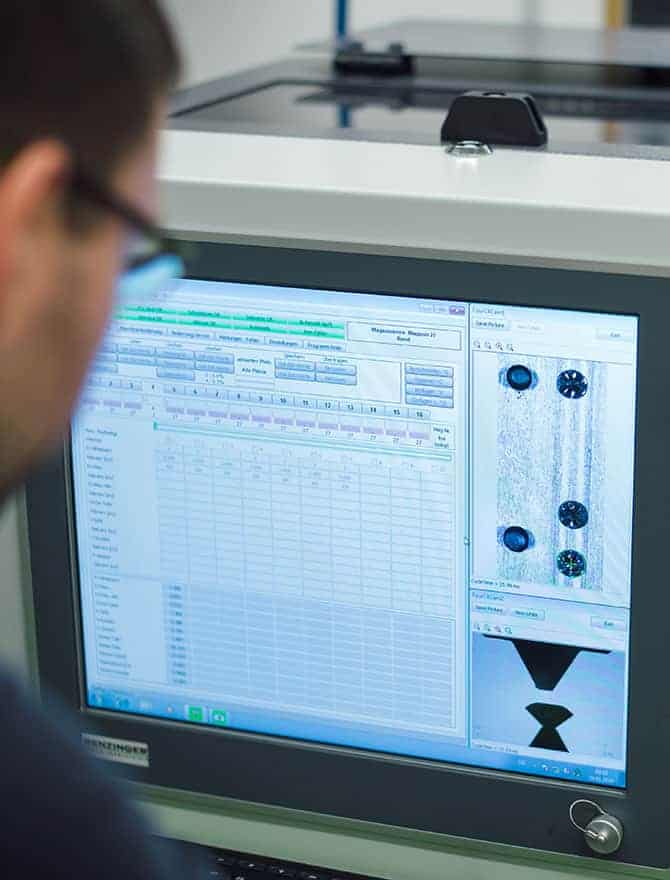
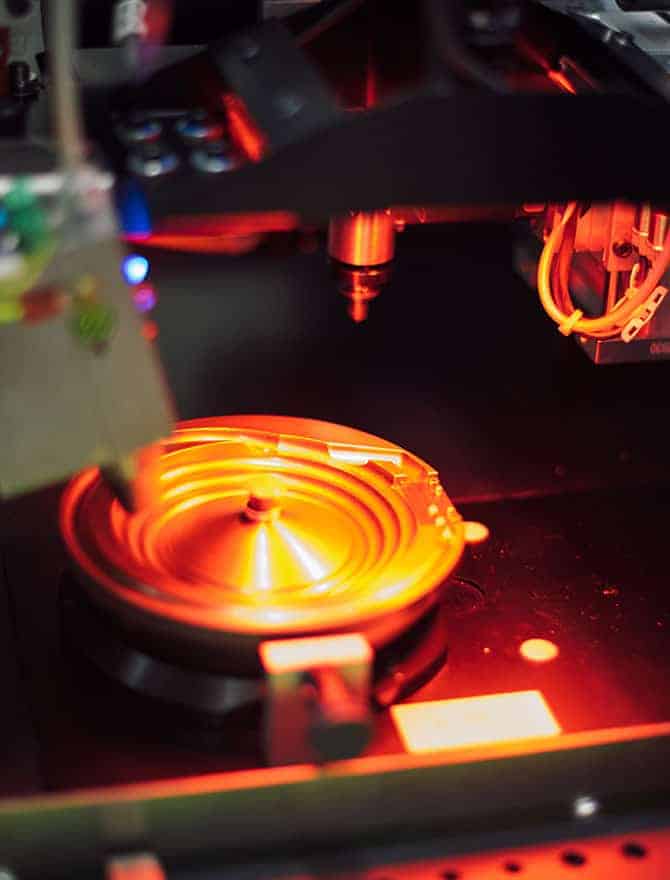


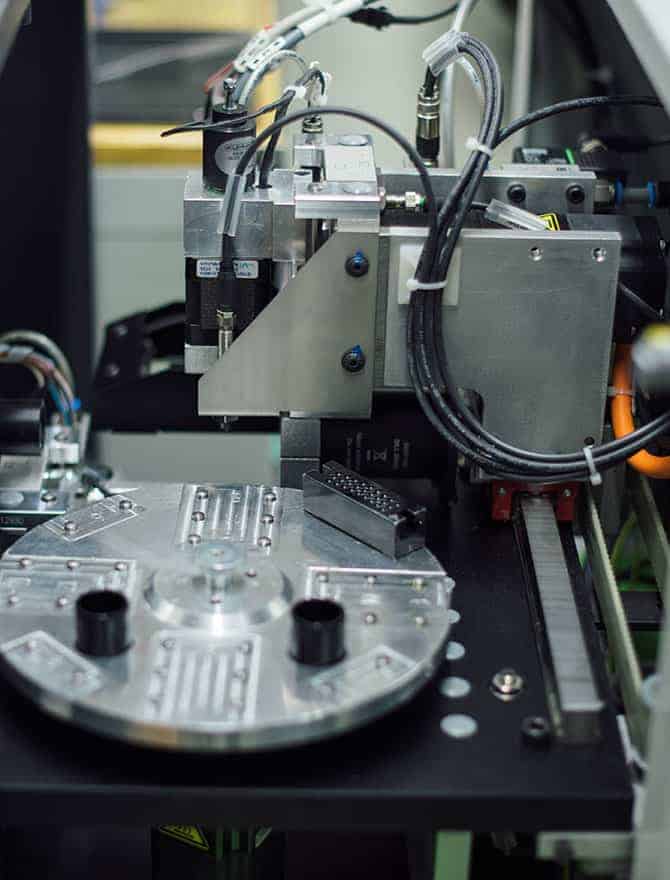
In order to achieve the highest possible quality, we rely on the close interaction of the most modern technology and real craftsmanship with diamonds as well. In order to determine ideal stones for certain applications in order to set them partially automatically in a later work step, we rely on automatic, digital stone measurement with the Benzinger FourC stone measurement machine.
Types of gemstones
Diamonds
A diamond is the cubic, crystallized modification of carbon. The diamond is the most valued gemstone. Due to its high color dispersion and refraction, it sparkles vividly. The most valuable and beautiful stones are transparent and clear like fresh spring water, but yellow, green, blue and black stones also occur in nature. Each gemstone only receives its true beauty through its cut.
Brilliants
Brilliants are diamonds that have a special cut (at least 32 facets in the upper part plus the table and at least 24 facets in the lower part). The designation brilliant is only permitted for round cut diamonds, all other gemstones with a brilliant cut must always use their mineral name (e.g. zircon brilliant / brilliant cut zircon).

Facet cut
With a facet cut, the stone is cut into a shape with several geometric surfaces (usually triangles and squares), which are called facets.
Brilliant cut
A diamond is the highest quality form of precious cut. Its shape consists of an upper and a lower part, which converge on the so-called "Rundist". With a regularly cut stone, the height of the upper part is a third. In the case of a perfect cut - also called triple good - the upper part 32 and the lower part 24 have surfaces - also called facets. This cut is mostly used for gemstones that are larger than 0.04 ct. Diamonds from 0.0625 ct to 0.025 ct are usually cut in which the upper part 16 and the lower part also show 16 facets, which is also referred to as double good. Gemstones from 0.04 ct to 0.0033 ct are given a cut in which the upper and lower part has 8 facets, which is also called "octagonal cut".
Baguette cut
With a baguette cut (also known as a long square or senale), the stone is given a very narrow, rectangular shape.
Princesss
Like the brilliant cut, the princess cut is of very high quality and is characterized by its square shape. In contrast to the brilliant cut, the top horizontal straight surface (also called the table) in the princess cut is square, in the brilliant cut this surface is round or a "squared circle" - a rounding with many edges.
Fantasy cut
With this cut, there are no limits to the name according to the imagination of the cut. Gemstones in different shapes such as hearts are often used for wedding rings.The quality criteria for diamonds are referred to as the 5 Cs: These mean carat, color, clarity, cut and conflict.
Carat
Carat describes the total weight of the gemstone. One carat has 0.2 grams and is abbreviated as ct. This unit of measurement arises from the fact that the seeds of the carob tree were previously used as a unit of measurement due to their similar weight of approx. 0.2 g and their same size. The term carat is not only used for the weight of gemstones, but also for the designation of how much gold there is in a gold alloy.You can find more about our precious metal alloys and the use of Carat in this context here .
Color
Another important quality criterion for gemstones is the color. The most valuable color would be absolute colorlessness and crystal clear transparency, which, however, does not occur in nature. For this reason, diamonds are divided into the following color categories (extract):- Very fine white (River)
- Fine white (Top Wesselton)
- White (Wesselton)
- Slightly tinted white (Top Crystal)
- Tinted white (Crystal)
- Tinted 1 (Top Cape)
Clarity
The value of a gemstone is measured further on the basis of its purity, its "clarity". When gemstones are formed in nature, these can contain inclusions, which can be solid, gaseous or even liquid. The purity of gemstones is categorized using the following terms:if - internally flawless - flawless, only possible surface traces from processing
vs1 / vsi - very small inclusions - inclusions difficult to see when magnified ten times
si1 / si - small inclusions - inclusions are easy to see at ten times the magnification.
Cut
The sparkle of a diamond, also known as fire, is significantly influenced by its cut. The different types of cut make the diamond sparkle in different ways.
Conflict
An important characteristic for a gemstone is its origin. Diamonds from conflict regions, also known as "blood diamonds", are sometimes extracted under inhumane circumstances. For this reason there are clearly marked conflict-free diamonds - accordingly the 5th C of the quality criteria stands for "conflict". Conflict-free diamonds are characterized by precise indications of origin.
The following diamond qualities are processed by us:
TW / if
Color: TW (Top Wesselton - fine white)Clarity: if - internally flawless - flawless)
TW / vsi
Color: TW (Top Wesselton - fine white)Clarity: vs1 / vsi - very small inclusions - very small inclusions
W / vsi
Color: W (Wesselton - white)Clarity: vs1 / vsi - very small inclusions - very small inclusions
Retailer information
Your advantages as a Merkle partner:
- Very experienced gem setters
- All types of stone settings (not all listed here, feel free to send us a request)
- Many years of expertise in setting special stones (largest diamond set so far: 15ct)
- Proven high quality of the diamonds used
- Exclusive use of diamonds from reputable suppliers (no conflict diamonds)
- Individual design options and different setting types are possible directly in our configurators
- Many years of experience in repairs and complex restorations
- Would you like to find out more? Please do not hesitate to contact us!
